 AduHid - Borland C Example AduHid - Borland C Example
This example uses the Borland C++ 5.5.1 compiler. Download a free trial of Borland C++
Builder from the www.borland.com web-site (unless Borland has recently changed their
policies).
Granted it is a command-line compiler but the price is right.
This example shows the steps to compile a simple application to communicate with an ADU
USB device.
Install the Borland Compiler
Download and install the Borland compiler onto the computer.
Create A Project Directory
Create a directory to hold the project. Here it is called "g:\Borland".
Copy the following files into the project directory.
- AduHid.h
- AduHid.lib
- AduHid.dll
Convert AduHid.lib To OMF
The AduHid.lib is distributed in COFF format. The Borland C++ compiler chokes on COFF
files. Fortunately Borland supplies a program that converts COFF files to OMF format.
In a DOS Command Window run:
Coff2Omf AduHid.lib AduHidOMF.lib
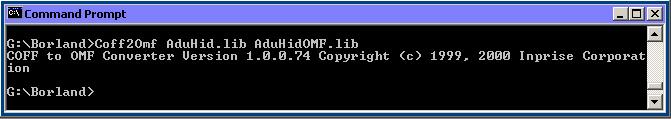
Note: to avoid contravening the Borland copyright we do not distribute the OMF file
created by this step.
Create The Source Code
Use a favorite editor to create the source code file.
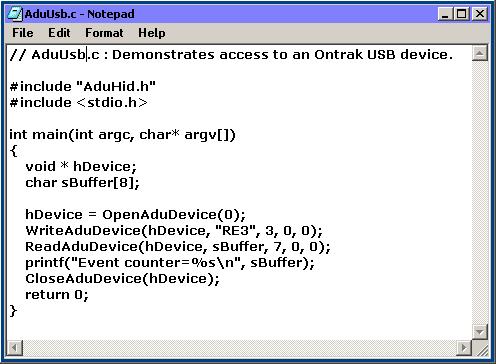
Compile and Run The Source Code
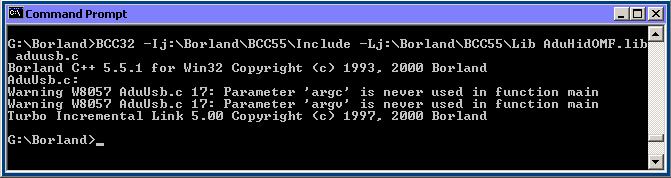
In a DOS Command Window:
navigate to the directory containing the source code
run the following compile command.
BCC32 -Ij:\Borland\BCC55\Include -Lj:\Borland\BCC55\Lib AduHidOMF.lib aduusb.c
(In case the above line is too long for the browser here it is in pieces)
BCC32 -Ij:\Borland\BCC55\Include
-Lj:\Borland\BCC55\Lib
AduHidOMF.lib aduusb.c
Note: The Borland compiler demo on this computer is installed in j:\Borland\BCC55. The -I
parameter points at the Include sub-directory. The -L parameter points at the Lib
sub-directory. Adjust the command to match the compiler directory on the computer being
used.
Note: the command must be entered as a single line on the DOS Command window.
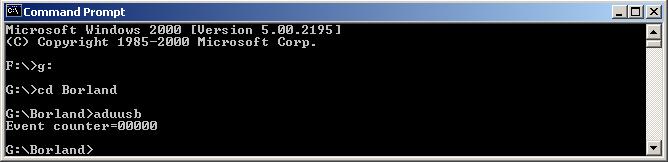
Run the program from the DOS Command window.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Mr. Borland for developing the compiler used in this tutorial. |